Goal 5: Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls


Article 16 of the Iraqi constitution stipulates equal opportunities for all Iraqis, and the state guarantees the necessary procedures to achieve this. National legislation does not include any discrimination between the sexes, and laws that guarantee equitable rights for women are still in force and in force. The most important achievements in this goal are:
- Establishing a department to empower Iraqi women in the General Secretariat of the Council of Ministers by Cabinet Resolution No. 333 of 2016 This department adopts a strategy to advance the status of Iraqi women and another one that deals with rural women.
- Forming the Special Investigation Court to look into human rights violations, including violations against women.
- Establishing a gender division in all Iraqi ministries.
- Establishing a women’s care and protection department in the Ministry of Labor and Social Affairs.
- Legislation of the Anti-Human Trafficking Law includes 8 articles that prevent the exploitation of children and women.
- The Labor Code includes clauses to criminalize and punish harassment.
- Adoption of a quota for women in the election law for Parliament, as well as for provincial councils.
- Iraq’s ratification of the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women (CEDAW), the Convention on the Rights of the Child and other related conventions.
- Legislation of the new Social Protection Law No. (11) of 2014 to limit violators of public money and reach families living below the poverty line.
- Emphasis on the application of the Personal Status Law, which prohibits marriage outside the courts and underage marriage in order to preserve the health of the mother and to ensure a good education for her children.
- Emphasis on reducing the rates of violence committed against women and girls, and there is a law under approval in the House of Representatives.
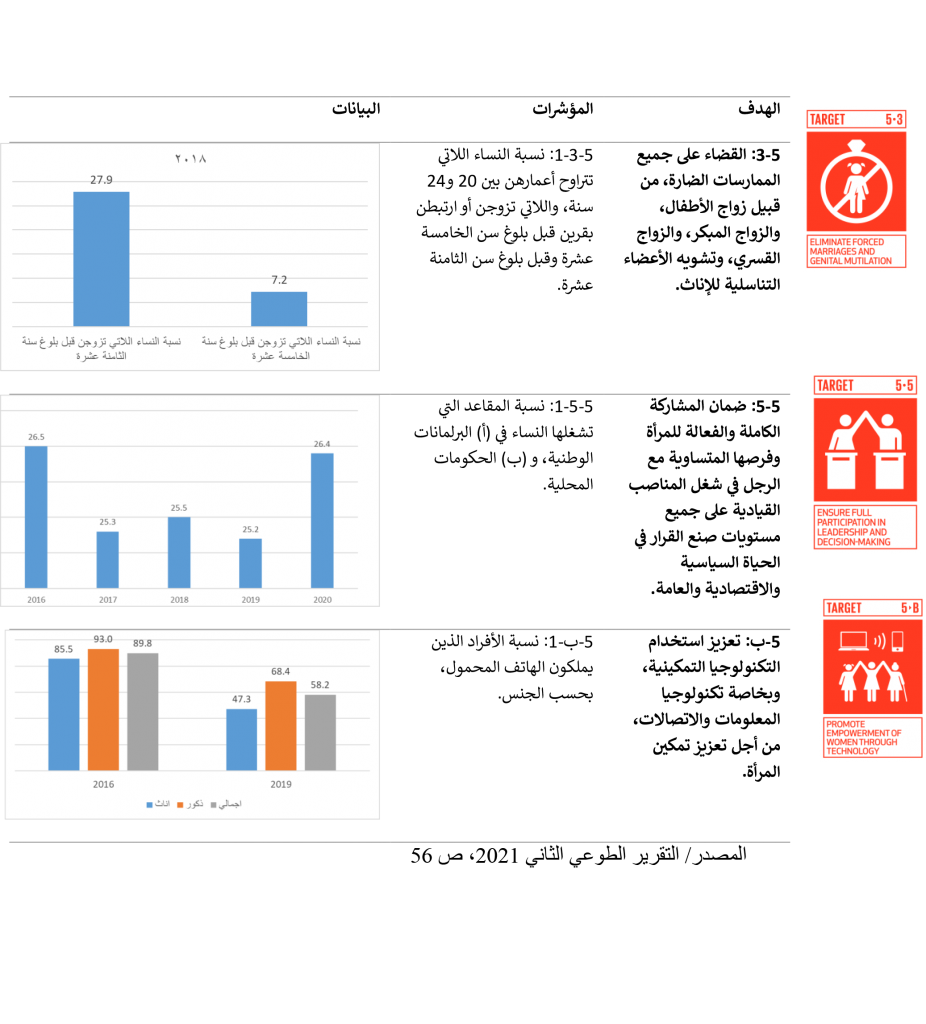
- n the field of labor-related legislation, the government issued the new Labor Law No. 37 of 2015, to reflect the state’s commitment to gender equality and to address discrimination against women in the labor market and to ensure equal pay with men that is in line with international labor standards, especially the basic principles and rights at work, which It was approved by the International Labor Organization, including the Maternity Protection Convention No. 183 for the year 2000. The following figure shows the most important indicators of the goal: